Su-33 Flanker
Originally a part of the aircraft selection in LOMAC, the Su-33 was ported over to DCS through the FC3 package.
Just like the other FC3 planes, the Su-33 is more designed to be controlled through a standardised set of keyboard shortcuts than through any kind of advanced set of peripherals, nor does it feature an interactive “clicky” cockpit. It stands out among the FC3 aircraft as being meant to operate from the Admiral Kuznetsov aircraft carrier with its angled ski-jump takeoff ramp.
Features
The Su-33 is a naval variant of the Su-27, and as such has a very similar features list:
- The same active radar and passive IRST guidance as the MiG-29 in terms of operation, but improved in actual capability.
- Medium-range semi-active R-27ER and IR-guided R-27ET missiles for BVR combat.
- A helmet-mounted target designator for high-angle, off-axis target locking.
- Tactical data linking that displays detected enemy and friendly aircraft along with navigation data on the HDD.
- In-flight refuelling capability.
- Strengthened landing gear and arrestor hooks instead of the Su-27's drag chute.
- Fancy little canards.
Comes with the built-in campaigns Su-33 - Heavy Sky and Su-33 Sea Dragon.
Flying the Su-33
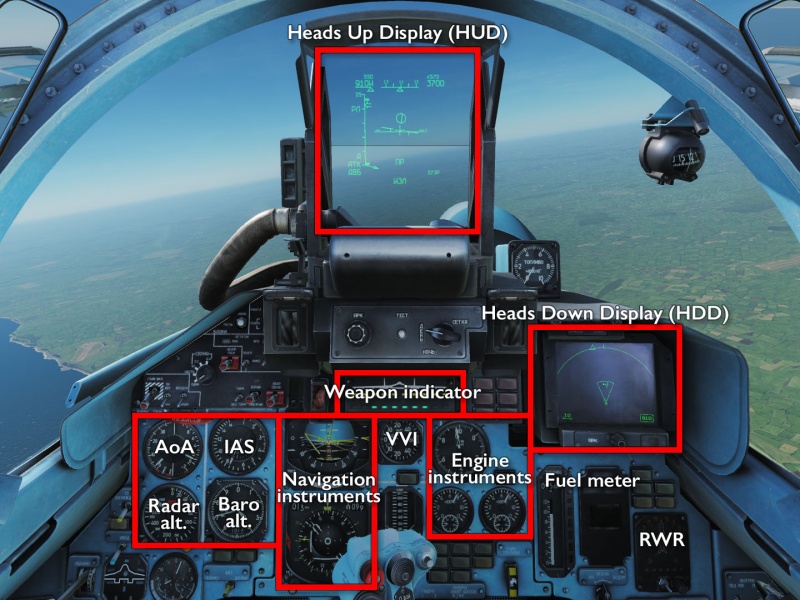
Cockpit overview
Getting into the air
The process of getting the Su-33 into the air is the same as with all FC3 aircraft:
- Make sure you have loaded the correct weapons and filled up on chaff, flares, and fuel.
(This can only be done with the canopy open and engines off, press LAlt-' to open the outfitting menu.) - RShift-L to turn the power on.
- LCtrl-C to open or close the canopy, as needed.
- RShift-Home to start both engine at the same time.
(RShift-End stops both engines; RAlt/RCtrl-Home/End starts and stops the left and right engines individually.) - Wait for the engines to spool up and stabilise.
- Num+/- controls the throttle; increase it carefully to get going and do not go too fast.
(W controls wheel brakes; be particularly careful when turning since doing it at high speed will make you tip over, scrape your wings, catch fire, explode and — worst of all — become the subject of innumerable screen shots.) - Use Z and X to control nosewheel steering (and also rudder) to make your way to the runway and line up.
- LShift-F lowers the flaps — they should be in the middle position for takeoff.
- Throttle up to max and try to stay in a straight line as you barrel down the runway.
- Pull back gently to take off.
- Raise landing gears with LCtrl-G; raise flaps with LCtrl-F.
Shooting something
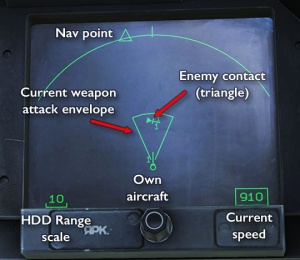
Since the Su-33 uses the same systems and weapons, employing it in air-to-air combat is the same as the MiG-29 and Su-27. The main difference over the procedure in the older MiG-29 is the data linking of targets and of navigation information that is shown on the HDD, along with the current sensor sweep area and the effective engagement range of the currently selected weapon, all of which offers a more visual way of finding and manoeuvring into firing position relative to your target.
- Press 2 to enter BFR master mode.
- Press D to select a missile type.
- Turn radar (I key) or electro-optical systems (O key) on.
(If using the radar, you can also use RAlt-I and RShift-I to change the tracking mode and frequency.) - Use RShift-, and RShift-/ to shift the scan zone left or right to where you expect the target to be.
- Based on GCI or AWACS information, use RShift-; and RShift-. to set the predicted relative altitude (in meters), and RCtrl-- and RCtrl-= to set the predicted range to the target.
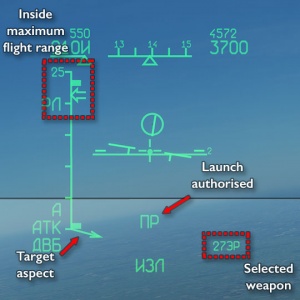
(When using the radar this filters targets and sets the elevation of the radar antenna. In IRST, the range is fixed, but elevation can still be changed.) - If a potential target is detected, dotted lines will appear on the HUD — the more dots, the larger the target; the higher up on the HUD, the longer the range.
(If using the radar, IFF will also be in effect: a double line means a friendly target; a single line means enemy.) - Use the ; , . and / keys to move the TDC over to a target. Press Enter to enter single-target tracking.
- On the right side of the HUD, bars will indicate the launch zone of the selected weapon.
- If launch parameters are met, “LA” (“ПР” in Russian cockpits) will be displayed.
(If IFF is used, launch request will be denied for any friendly targets.) - Press Space to fire.
(If using a semi-active radar missile like the R-27R or -ER, you must maintain STT lock-on until the target is hit.)
Once in the merge, you will probably want to switch to one of the close-range master modes, like longitudinal mode (6 key) or HMD mode (5 key) and use those in conjunction with the radar (I key) to lock and engage targets.
More information
- Sukhoi Su-33 on wikpedia.
- Su-33 (Su-27K) on globalsecurity.org