Lessons: Difference between revisions
(→�) |
(→�) |
||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
# Magnetic Bearing = True Bearing - Declination | # Magnetic Bearing = True Bearing - Declination | ||
# Magnetic Bearing = 043 - 6 | # Magnetic Bearing = 043 - 6 | ||
# Magnetic Bearing = | # Magnetic Bearing = 037 | ||
===Bonus: Heading, Bearing, Course, and Track=== | ===Bonus: Heading, Bearing, Course, and Track=== | ||
Revision as of 04:15, 13 January 2022
AIR GOONS NAVIGATION COURSE - DON'T BE A WAYPOINT CRIPPLE
Goofus flies in the general direction of the target, wasting time and fuel when he gets lost.
Gallant flies straight to where he means to, filled with confidence and vigor.
Lesson 1: Magnetic Declination
Has the following ever happened to you? You're trying to fly to a particular point. You open the F10 Map and use the ruler tool to measure the bearing and distance between your aircraft and that point. You turn to the bearing you measured, but despite carefully tracking that heading, you still find yourself noticeably off course. There wasn't even any wind in the mission. What happened?
True vs. Magnetic Heading
The ruler tool in the DCS World Map and Mission Editor gives you True Heading measurements. However, almost all navigation systems display Magnetic Heading (some are toggleable).
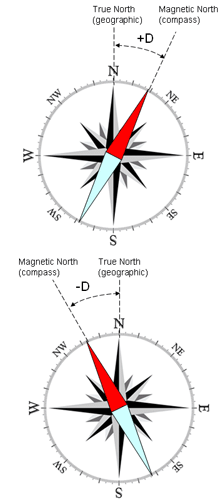
The difference between Magnetic Heading and True Heading is due to the difference in location between the Magnetic North Pole (formed by currents of molten iron in the Earth's core, currently located somewhere in Northern Canada) and True North Pole (Santa's House, the point around which the globe spins).
Magnetic Declination
Magnetic Declination is the difference in degrees between the Magnetic North and True North.
- When Magnetic North points East of True North, the sign of the deviation is Positive.
- When Magnetic North points West of True North, the sign of the deviation is Negative.
Note: Do not confuse Declination with Magnetic Variation, which caused by local effects of the airplane's metallic structure on the magnetic compass reading (not simulated in DCS).
How to Find Magnetic Declination
Magnetic Declination can be found on navigation charts. Some DCS modules show you the actual in-game declination either in avionics or on the kneeboard...
- F-14: Kneeboard (Ground Settings, MAG VAR)
- F-16: DED: LIST - 0 MISC - 2 MAGV
- F-18: HSI - DATA - A/C
- AV-8B: Kneeboard (Initial Position: 4. Magvar)
- Mirage-2000: PCN DEC
Magnetic Declination in DCS Maps
Magnetic Declination differs per LOCATION and TIME. The following are "close enough" approximations.
Magnetic Declination per Map in 2016 (Approximate)
- Nevada: +12
- Caucuses: +6
- Syria: +5
- Persian Gulf: +2
- Marianas: +1
Converting True to Magnetic
True Heading = Magnetic Heading + Magnetic Declination
Magnetic Heading = True Heading - Declination.
Example: Batumi to Kutaisi Flight
It's 2008 and you're on the DCS Caucuses Map. You want to fly from Batumi Airfield to Kutaisi Airfield. The True Bearing measured from the F10 map is 043 degrees. What is the Magnetic Bearing?
- Magnetic Bearing = True Bearing - Declination
- Magnetic Bearing = 043 - 6
- Magnetic Bearing = 037
Bonus: Heading, Bearing, Course, and Track
- Heading is the direction the airplane's nose is pointed.
- Bearing is the direction between two points.
- Course is very similar to bearing. It's the desired direction you want to fly. If you're flying directly to a point, your course is the same as its bearing.
- Track is actual path the airplane takes across the ground. It's affected by wind and navigational inaccuracies.